Secondary Research Services: A Complete Guide to Strategic Market Analysis
In today’s data-rich environment, businesses rarely struggle with access to information. Instead, the real challenge lies in organizing scattered data into clear, decision-ready insights. Secondary Research Services help organizations interpret existing information systematically and transform it into structured intelligence for strategic planning.
This guide explains what Secondary Research Services are, how they work, when they are used, and their advantages and limitations.
What Are Secondary Research Services?
Secondary Research Services involve analyzing existing data sources to answer business questions—without conducting new surveys, interviews, or field studies.
Rather than gathering fresh (primary) data, secondary research relies on previously published or recorded information and applies structured methodologies to extract insights.
Core Elements of Professional Secondary Research:
Defining the specific business objective
Identifying relevant and credible data sources
Collecting and organizing available information
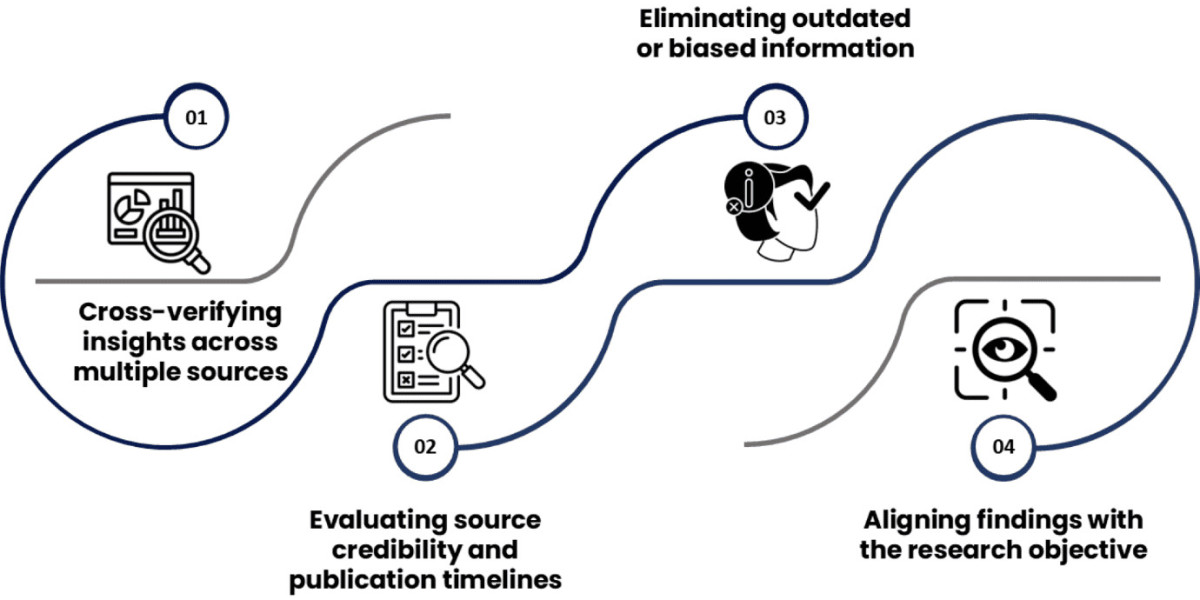
Cross-validating findings using triangulation
Documenting assumptions and limitations
Presenting structured, decision-focused outputs
The objective is not just data collection, but building reliable intelligence that supports informed decisions.
When Do Businesses Use Secondary Research Services?
Organizations typically use secondary research when they need cost-efficient, timely, and evidence-based direction.
1. Market Entry and Expansion
Before entering a new region or industry segment, companies often need clarity on:
Market demand and growth potential
Regional performance variations
Regulatory considerations
Distribution and route-to-market models
Secondary research provides an initial evidence base to evaluate feasibility before committing resources.
2. Competitive Intelligence
Secondary research helps analyze competitor activities such as:
Product portfolios
Pricing structures (where publicly available)
Partnerships and acquisitions
Hiring patterns
Expansion strategies
By identifying trends and signals, organizations gain a broader understanding of the competitive landscape.
3. Market Sizing and Demand Estimation
Market sizing often requires combining multiple datasets to estimate:
Total market value
Growth rates
Serviceable available market (SAM)
Serviceable obtainable market (SOM)
Where data transparency is limited, triangulation methods help create reasonable ranges and scenario models.
4. Investment and Strategy Evaluation
Investors and strategy teams use secondary research to assess:
Industry structure and value chains
Margin dynamics
Demand drivers
Structural and regulatory risks
This supports more informed capital allocation decisions.
5. Procurement and Supplier Mapping
Secondary research also supports:
Supplier landscape analysis
Certification and compliance checks
Capacity indicators
Risk screening
This allows companies to evaluate potential suppliers before initiating direct engagement.